Gateways
In process management—specifically in BPMN—gateways are considered decision points, branches, and merges in the process flow and are represented graphically in a diamond shape. They enable the mapping of business rules and parallel processes. This allows complex process logic to be represented clearly and in a standardized manner.
What types of gateways are there?
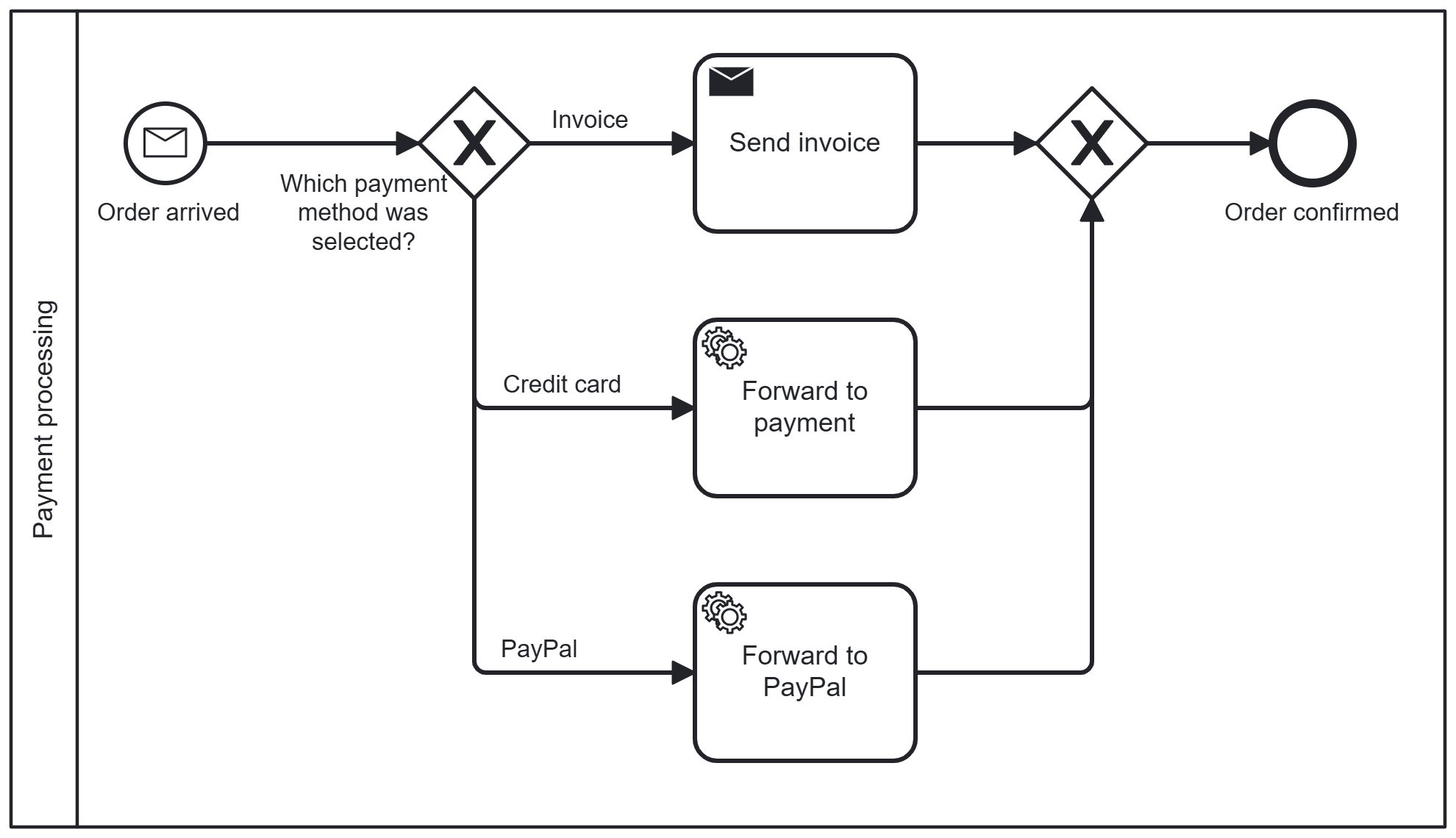
Exclusive gateway (XOR)
This gateway represents an either/or decision – exactly one path is taken.
Example:
When shopping online, you choose a payment method: invoice, credit card, or PayPal. Only one option can be executed.
Ideal when a process should take only one possible path depending on the condition.
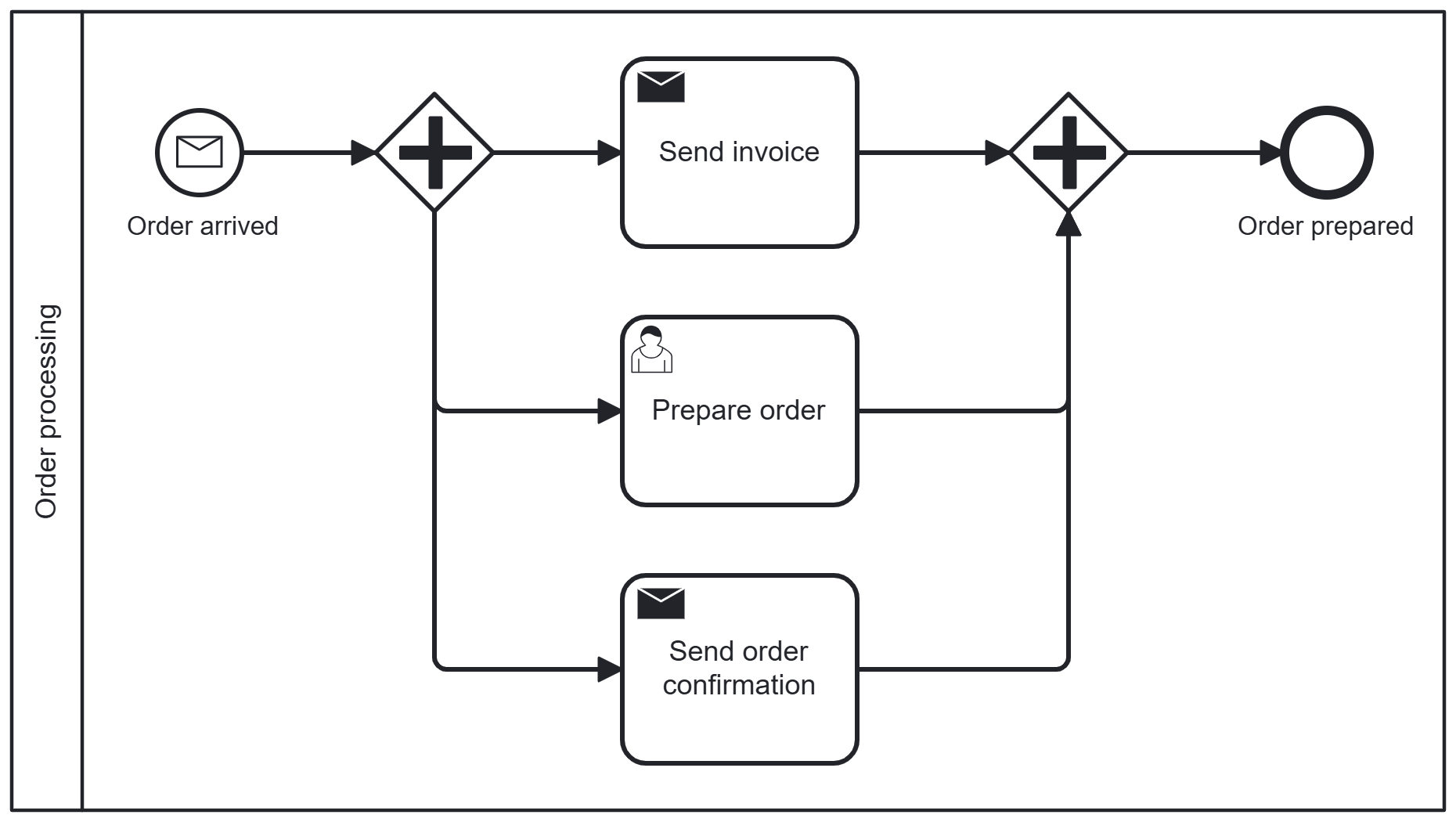
Parallel gateway (AND)
With parallel gateways (AND), multiple paths start simultaneously and wait at the end until all are complete.
Example:
After the order is received, several tasks are executed in parallel:
- Send invoice
- Prepare order
- Send order confirmation
Only when all tasks are completed is the order considered prepared.
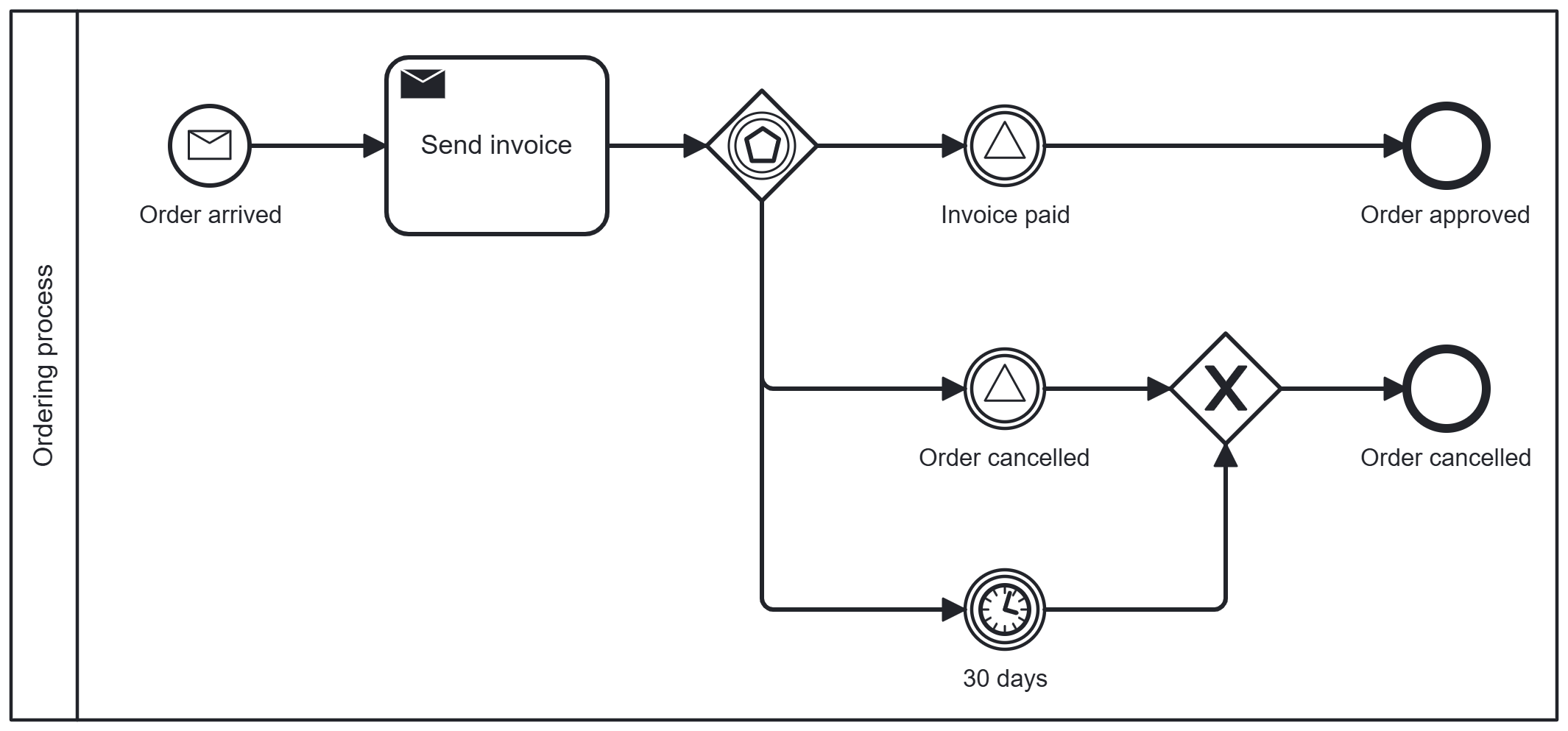
Event-based gateway
The event-based gateway waits until a specific event occurs before continuing the process.
Example:
After the invoice is sent, the system waits to see whether payment is received or the order is canceled. If no payment is registered within 30 days, the order is automatically canceled.
This gateway is used when the process depends on external events, such as a message, deadline, or action.
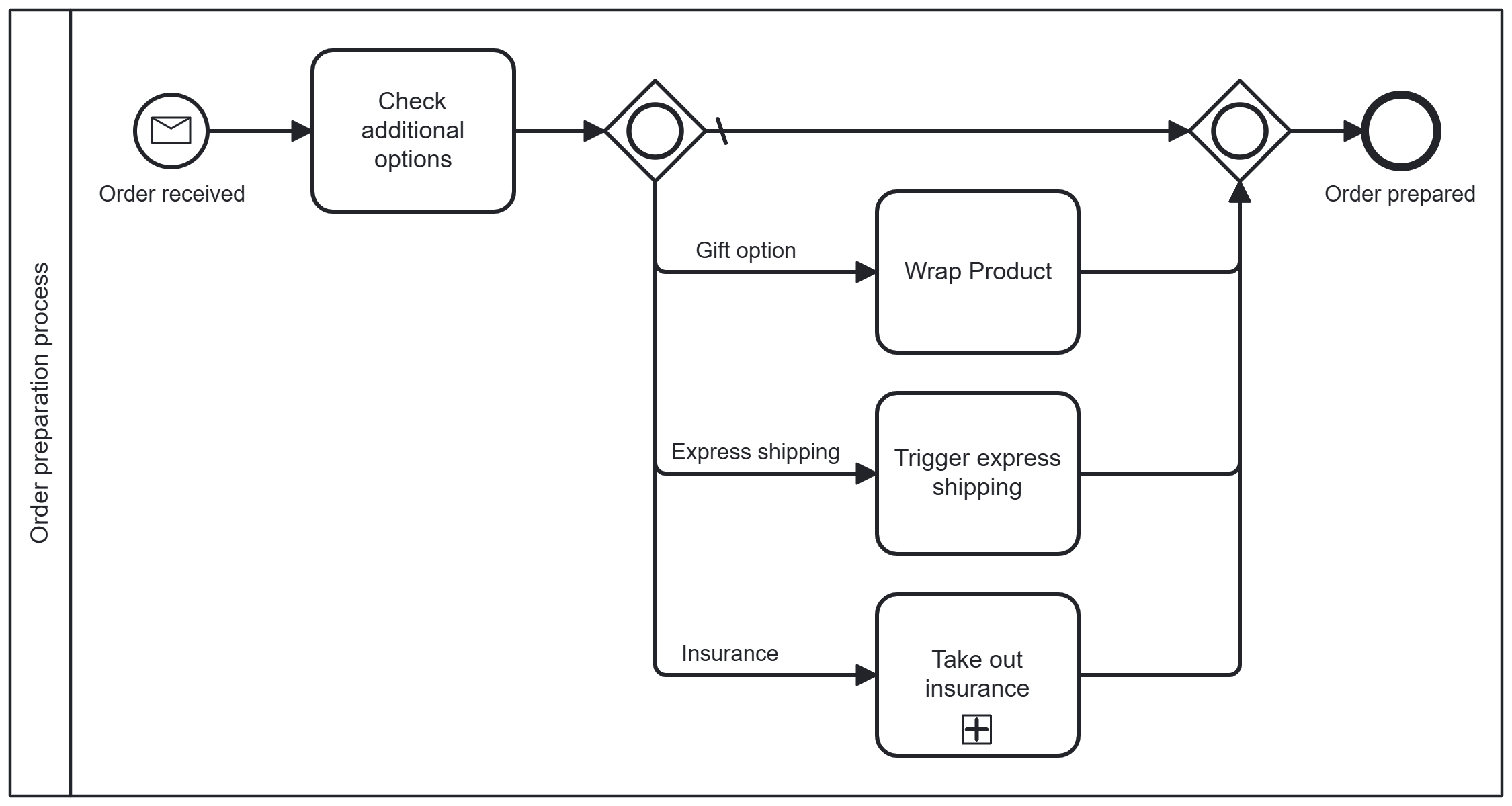
Inclusive gateway (OR)
With the inclusive gateway (OR), one or more alternative paths can be selected simultaneously, depending on what applies.
Example
The process checks whether the buyer has selected additional options such as gift wrapping, express shipping, or insurance. All selected options are executed in parallel. Once these are complete, the order is prepared.
Ideal when different requirements need to be met simultaneously, e.g., for additional services or extra features.
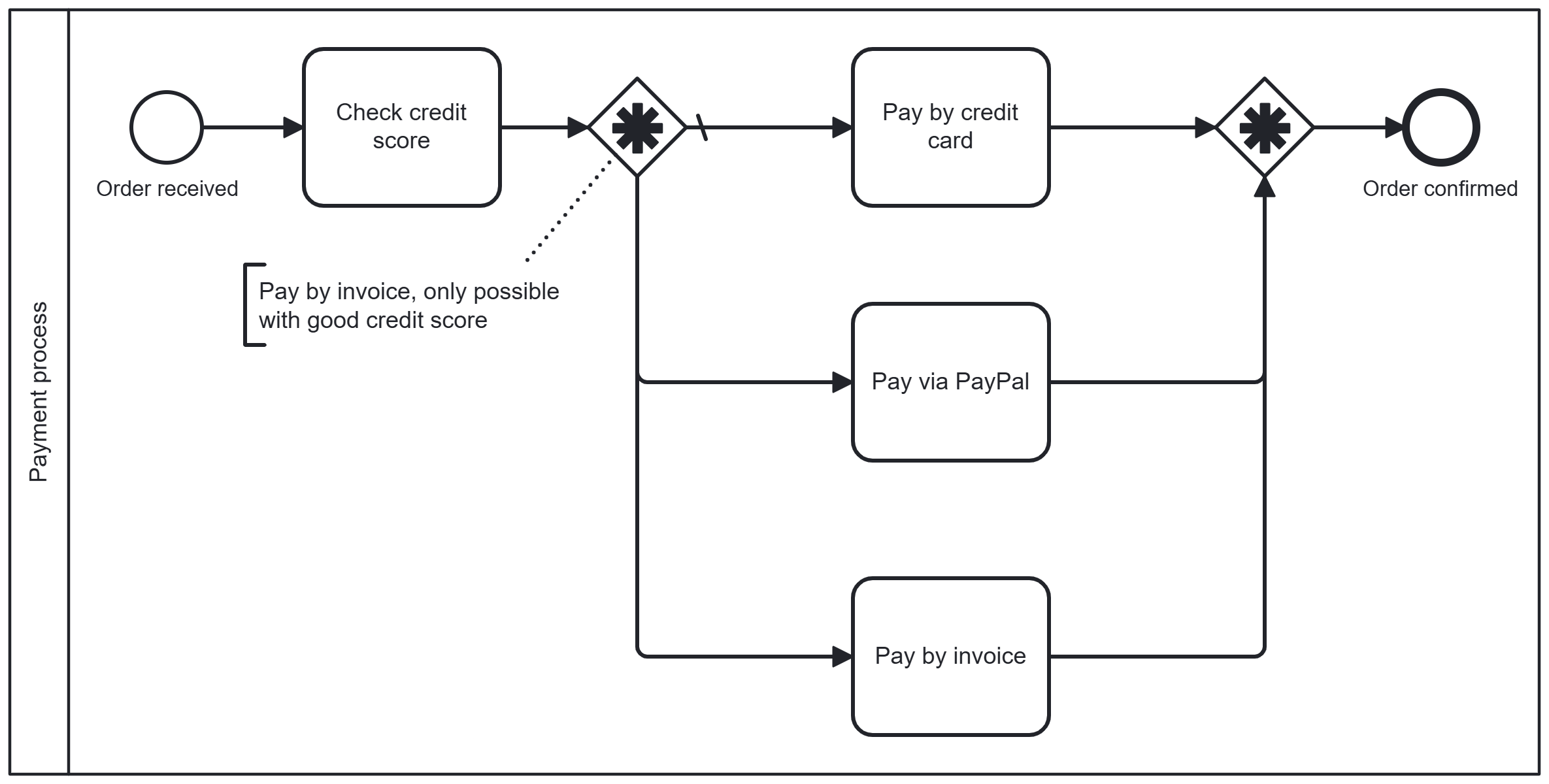
Complex gateway
The complex gateway is considered a special solution for complicated logic. It is used when simple conditions are not sufficient.
Example:
The reliability of a customer's payments is checked. If their credit rating is good, they can pay by invoice. If their credit rating is poor, only credit card or PayPal are available as payment options.
This gateway allows the mapping of multi-level conditions that cannot be represented with XOR, OR, or AND.
Conclusion
Gateways are a central element of process modeling: They provide clarity when decisions have to be made, processes have to be parallelized, or brought back together. This keeps processes understandable, transparent, and free of logical errors.